Ours is a holistic approach that does not hinder the physiological processes of the body. It's an approach that encourages the restoration of balance, by combatting the causes of symptoms as efficiently as possible and ensuring fast relief.
Symptoms and relief
SELECT YOUR NEED
Liver
OUR BODY'S DETOXIFYING POWERHOUSE
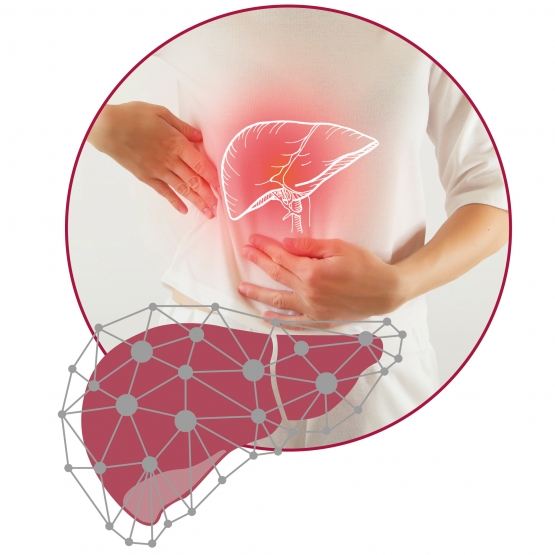
When a physical disorder arises, in addition to treating the symptoms, we should identify the source of the problem. It is very often the case that one of the main excretory organs is involved: THE LIVER.
THE LIVER
The liver is the largest excretory organ in the body, weighing about 2 kg and performing crucial functions for our health. It is located on the right side of the abdomen, below the diaphragm.
Its importance was already known in ancient times: the Greeks believed that the liver was the seat of courage, hence the expression 'lily-livered' meaning 'fearful'.
ITS FUNCTIONS
- METABOLIC FUNCTIONS: in addition, it performs numerous functions related to carbohydrate metabolism.
- SYNTHESIZES ENDOGENOUS CHOLESTEROL, its respective transport proteins (LDL, HDL, VLDL) and triglycerides.
- PRODUCES COAGULATION FACTORS I (fibrinogen), II (thrombin), V, VII, IX, X and XI, as well as protein C, protein S, hepcidin and antithrombin.
- PRODUCES SERUM PROTEINS, essential for the transport of metabolites in the bloodstream and for the functioning of the veno-lymphatic system (one of which is albumin).
- PRODUCES PEPTIDES crucial for the regulation of blood pressure (angiotensinogenic).
- METABOLIZES MANY TOXIC SUBSTANCES, drugs and hormones (especially steroids).
- CONVERTS AMMONIA TO UREA as an end product of protein metabolism.
- ACTS AS A STOREHOUSE for numerous substances, including glucose (in the form of glycogen), vitamin B12, iron and copper.
- PRODUCES RED BLOOD CELLS: This is the main site of their production in the fetus. It is replaced in this task by the bone marrow at 32 weeks of gestation.
- PRODUCES AND SECRETES BILE, essential for emulsifying lipids introduced through the diet, which also include vitamins and other substances essential for life.
BILE ACIDS
The major constituents of bile are bile acids, end products of hepatic metabolism of cholesterol. They are essential for blood sugar regulation, but not only:
- DCA (deoxycholic acid) has shown both significant antibacterial effects and protective action on the intestinal barrier.
- LCA (lithocholic acid) is able to activate the receptor for intestinal vitamin D, promoting a local anti-inflammatory effect.
- UDCA (ursodeoxycholic acid) has an anti-inflammatory and protective role in neurological disorders such as Parkinson's, Huntington's, and Alzheimer's.
WHICH ISSUES ARE RELATED TO THE LIVER AND WHY?
Given the variety and importance of its functions, the health of the liver is closely associated with the overall health of the body.
Bad habits cause a buildup of waste substances in the liver, resulting in a slowdown or alteration of its physiological functions.
This functional overload can predispose a person to the onset of several problems, such as:
- ALTERED NUTRIENT ABSORPTION: impaired bile flow and poor digestive performance, causing malabsorption of various nutrients.
- INTESTINAL DYSBIOSIS: pathological alteration in the composition and function of the intestinal microbiota, the symptoms of which may include constipation, dysentery, abdominal bloating, etc.
- BILIARY DYSPEPSIA: altered motor function of the bile ducts, resulting in slowed digestion.
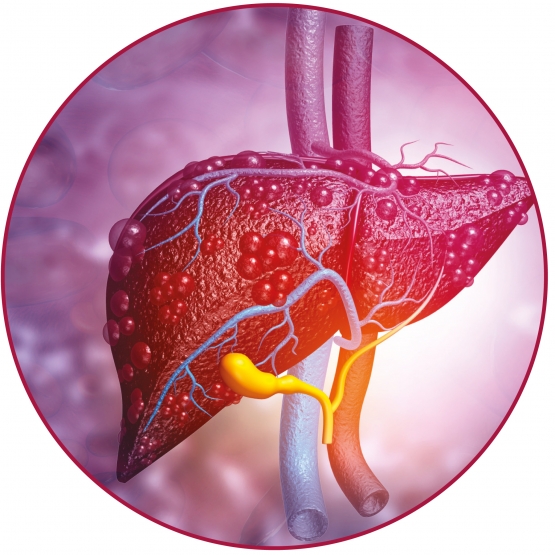
- HEPATIC STEATOSIS: accumulation of fat in the liver tissue (so-called 'fatty liver'), leading to overload for the liver cells and, if not corrected, cell damage.
- ALTERED BLOOD SUGAR REGULATION: onset of insulin resistance and type II diabetes.
- ALTERED LIPAEMIA: alteration in the circulating lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides).
THE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM OF THE LIVER
In many of its functions, the human body is regulated by precise biological cycles. The main reference period is 24 hours, during which most of the physiological changes, called 'circadian', can be accounted for.
A more or less extensive alteration of these rhythms is linked to numerous pathologies (metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular events, inflammatory bowel diseases), because it is able to influence metabolic, hormonal, and neurological parameters.
Like other organs and metabolic processes, the liver also exhibits functional rhythms that vary throughout a 24-hour period, according to the time of day. In particular, it exhibits two distinct phases of activity:
- BILIARY PHASE: from about 1 p.m. to 9 p.m., high levels of C4, a precursor of bile acids, can be found in the blood, indicating an intense bile production phase.
- METABOLIC PHASE: during the night there are high levels of lathosterol (the main precursor of cholesterol synthesis), a sign that the liver is engaged in the synthesis of this key lipid.
HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTION
MILK THISTLE AND SILYMARIN
Milk Thistle extracts promote liver regeneration. Silymarin is effective in protecting the liver from damage induced by exogenous substances (especially alcohol and drugs) and exhibits potent antioxidant activity on liver tissue.
ANTIOXIDANT ACTION
ARTICHOKE, SILYMARIN AND VITAMIN E
Silymarin has antioxidant properties tens of times more potent than vitamin E, with an effect concentrated on liver cells. Another extract with antioxidant action which has marked activity on the liver is Artichoke extract, rich in simple and complex flavonoids.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTION
GINGER, SILYMARIN
Ginger extracts are endowed with marked systemic anti-inflammatory activity, which combines with that of Silymarin, whose action instead focuses on the liver. In addition, they have the ability to attenuate the course of chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the liver.

DIGESTIVE EFFECT
GINGER, ARTICHOKE AND ROSEMARY
Ginger, Artichoke, and Rosemary are known for their appetite-enhancing and digestive properties. In particular, ginger promotes stomach motility and smooth gastrointestinal muscle activity in general, thus providing effective antiemetic activity.

DIURETIC AND PREBIOTIC ACTION
DANDELION
Dandelion leaves, in addition to exerting a strong detoxifying effect on the biliary tract, are also characterized by a modest diuretic activity, confirmed by a recent pilot clinical study.
Dandelion root (containing inulin) has shown a prebiotic activity specifically directed towards certain strains of bifidobacteria, one of the most important and representative bacterial populations in our intestinal microbiota.
METABOLIC ACTION
INDIAN BARBERRY
Indian Barberry extracts, in phytosomal form, have an effect on hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic processes involving cholesterol and have a positive action on the recovery of the damaged intestinal barrier function.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY, ANTIFIBROTIC AND RELAXING ACTION
INDIAN PENNYWORT
Indian Pennywort is able to lower the levels of inflammatory mediators in the liver and also limit the production of collagen induced by inflammation.
One of the most used properties of Indian Pennywort is its anxiolytic and relaxing effect: hepatic overload can lead to waking up at night during the time slot characteristic of liver activity (between 2 and 3 a.m.), causing disruption to the body's circadian rhythms.

LIVER - LIFESTYLE - NUTRITION
A proper lifestyle, a healthy and balanced diet, and maintaining an appropriate weight, also involving adequate physical activity (at least for 30 minutes a day), are essential for the health of our body and our liver.
To maintain a healthy liver and help it perform its depurative function, it is important to pay attention not only to what you eat, but also to how much, when and how. The ideal regimen consists of a rich breakfast, a moderate lunch and a light dinner. Furthermore, it is a good habit to eat vegetables before main meals and to hydrate properly with water, infusions, herbal teas, decoctions, cold presses, smoothies, vegetable juices, flavored water, etc.
Finally, to avoid overstressing the "purification powerhouse," it is essential to know the consequences of certain behaviors.
- Excess sugar causes insulin spikes which "stress" the liver
- Excessive drinking of alcohol and spirits is the greatest damage that one can do to the liver
- Excessive consumption of processed white foods with high Glycemic Index (pasta, bread, 00 flour, baked goods etc.) causes insulin spikes. The cause can be traced to the high concentration of starches and sugars: excess consumption can "overload" the liver, resulting in the risk of insulin resistance and/or excessive production of endogenous cholesterol
- "Hydrogenated fats" typical of industrial products, when consumed for a prolonged time, stress and burden the liver.

Taking care of your purification powerhouse - having a healthy, well-purified and active liver - means giving yourself the chance to prevent many problems and diseases. The first step is to become aware that it is much easier to overload it than you think. Excess sugar, for example, stimulates the production of insulin that is partly responsible for an increase in endogenous (liver-produced) cholesterol. Considering that insulin spikes occur mainly as a result of eating meals with an unbalanced quantity of refined carbohydrates (sweets, sugar, pasta etc.), it is evident that by following a dietary approach that maintains balance between carbohydrates, proteins and fats, it is easier to keep cholesterol at bay, an issue that most laypeople erroneously associate with fat overconsumption alone. Therefore, in order not to overburden the liver, an essential step is to change habits by limiting the consumption of refined carbohydrates, especially at dinner, replacing them with alternatives that will be beneficial to the whole body in the long run.
SIMPLE AND HEALTHY SUBSTITUTIONS:
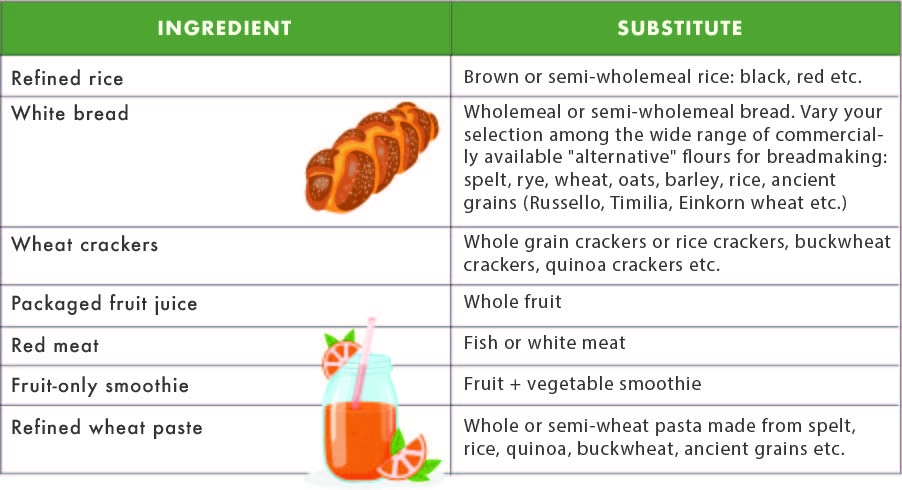
Which "detox" to choose?
The first "non-food" element of the depurative approach is water, to be drunk in an average amount of 2 liters per day. Among foods, the best choices are fruits and vegetables, which are rich in water and numerous beneficial substances such as antioxidants, vitamins, fiber and minerals, which "lighten" the body thanks to their ability to promote organ functionality, including that of the liver. A good habit is to supplement the consumption of vegetables and fruits with smoothies, centrifuges, extracts, etc.
Let's look at some suggestions for detox ingredients and associations:
- carrot + apple + ginger
- spinach + pineapple + mint
- fennel + carrot + turmeric + juice from 1 lemon
- red cabbage + carrot + ginger + pear

THE ADVANTAGES OF:
- ARTICHOKES: Thanks to the presence of cynarin, they regulate liver function and are among the most detoxifying foods for the liver; they also aid the diuretic and digestive function. Excellent when eaten raw in salads with oil, salt and lemon, or steamed or pan-fried
- PINEAPPLE: acts as a depurative due to the high presence of water and fiber
- LEMONS: to make the most of their known depurative effects, it is ideal to consume them in the morning on an empty stomach in the form of juice, diluted with warm water. IMPORTANT: Avoid consumption in the presence of gastritis or an irritated stomach
- CARROTS: just like fennel, they have a depurative and anti-bloating function. Best consumed raw and in combination with ginger
REMEMBER: There is currently no drug therapy for liver fatigue; the best treatment is to adopt a proper diet and lifestyle
- choosing foods of organic and/or 0-km origin
- following a varied diet, favoring the consumption of fruits and vegetables, preferably in season, easily digestible proteins (fresh small fish, white meat, eggs), legumes, pumpkin seeds, sunflower, flax, chia, etc., walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts, etc.
- consuming cereals, preferably whole grain but not only, because in some cases fiber prevents the absorption of minerals and other nutrients, semi-wholegrain cereals and pseudocereals (quinoa, buckwheat, amaranth)
- preferring foods that are sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as flax oil, hemp oil, oily fish (mackerel, sardines, sardines etc.), chia seeds, flax seeds, etc.
- staying adequately hydrated. Water requirements vary from individual to individual and change according to different lifestyles, the type of activity and the diet. An adult should generally drink 2 liters of water per day to maintain their health. Water is an essential element for the body because it regulates various biological functions. Therefore, it is important to maintain proper hydration, especially during the summer season, during sports activities and in all situations where a lot of fluids are lost.
- avoiding abuse of gluten-containing foods, packaged foods and fried foods
- limiting sugar, sugary drinks, refined grains (white bread, white pasta, white rice, etc.)
- avoiding hydrogenated fats, limiting red meat, milk and its derivatives, and salt. When consuming them, prefer those of high quality
The notions and advice offered herein are for educational purposes only and cannot under any circumstances replace medical advice. For a complete diet, it is necessary to consult a nutritionist, who, after appropriate clinical and instrumental examination, will be able to identify the needs of the person concerned and put together a personalized diet plan.