Ours is a holistic approach that does not hinder the physiological processes of the body. It's an approach that encourages the restoration of balance, by combatting the causes of symptoms as efficiently as possible and ensuring fast relief.
Symptoms and relief
SELECT YOUR NEED

Throat
The generic term "throat" is used for the anatomical tract in the front part of the neck, consisting of the pharynx, larynx and the upper parts of the trachea and esophagus; both the air we breathe and the food we ingest pass through these organic channels. As one can guess from the anatomical parts that make up the throat, it has no bone structure of its own and is instead supported by the skeleton of the neck, which lies immediately behind it.
Regarding muscles, the most important are the splenius and the sternocleidomastoid, both of which are stretched between the bones of the head and the sternum and cover the anterior part of the throat; the tongue, located inside the oral cavity, also plays an important part, having an essential role in swallowing and thus in ensuring the passage of food through the throat.
Major blood vessels also pass close to the throat, such as the carotid artery, which carries oxygenated blood to the brain, and the jugular vein, which carries oxygen-poor blood back to the superior vena cava. These two vessels are essential to the body's life, as they nourish the brain: this is why the throat is one of the most vulnerable parts in all animals, including humans.
The vocal cords, consisting of thin membranes, are located in the larynx and, together with the tongue, teeth and palate, form the vocal or phonatory apparatus. The Adam's apple is a protrusion of the thyroid cartilages of the larynx, whose function is to protect the larynx. The adenoids are part of the lymphatic system and serve to protect the airway from bacterial infiltration; they are located in the nasopharynx, the uppermost part of the throat. Finally, the epiglottis is a small cartilaginous membrane that is located between the pharynx, esophagus and larynx; thanks to an involuntary reflex, it closes over the larynx at the moment of swallowing and has the role of protecting the larynx against the entry of food during swallowing, closing due to pressure from the tongue.
The oropharyngeal cavity can always be subject to ailments caused by
- sudden changes in temperature
- contact with irritants
- microbial infections

OROPHARYNGEAL CAVITY PROBLEMS CAN OCCUR AT ANY TIME OF THE YEAR
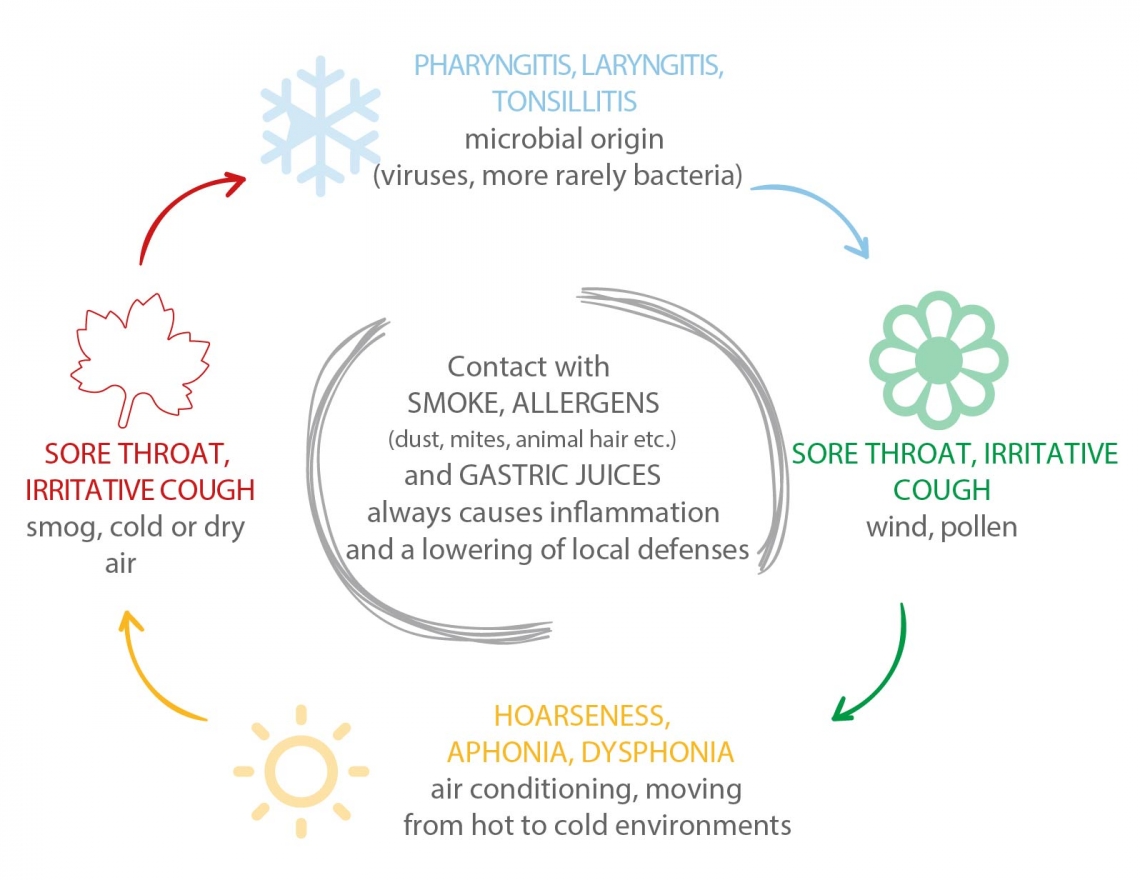
Pharyngitis is the inflammation of the pharynx, a muscular-membranous duct, approx. 15 cm long, located between the mouth and esophagus, where the airway and digestive tract begin, commonly referred to as the "throat." The throat can become inflamed and sore, not only due to viral causes (adenoviruses, enteroviruses, coronaviruses, infectious mononucleosis, rhinoviruses, influenza viruses, parainfluenza viruses, etc.) or bacterial causes (Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, etc.) but also due to irritants (smog, cigarette smoke, etc.).
The typical symptoms, in addition to an annoying sore throat, are: difficulty swallowing, cough, and catarrhal discharge.
Pharyngitis, from an initial acute phase, can become chronic if neglected or not treated with the appropriate remedies. This can have local causes, such as the obstruction of the nasal passages, smoking, alcohol, staying in dry places for longer periods, or it may be a consequence of other problems, such as tonsillitis, candidiasis, etc.
Chestnut
Chestnut leaves are rich in tannic substances in their glycosidic form, derived from gallic and ellagic acid. Chestnut tannins have strong antioxidant properties, which can reduce inflammation in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. Moreover, thanks to their ability to bind to mucosal proteins, these substances form a protective and soothing layer over irritated mucous membranes, due also to the synergy of the plant active ingredients in the product.
Lavander
Lavender flowers are very rich in terpene essential oils (geraniol, linalool, borneol, pinene, thymol), coumarins, and tannins and have traditionally been used for coughs, whooping coughs and respiratory tract infections due to their soothing and protective action. These active ingredients allow the plant to have a remarkable antispasmodic and relaxing effect on the nervous system; therefore, it is useful for calming nervous coughing fits.
Marrubium
The flowering tops of Marrubium contain a high amount of lactone diterpenes (of which marrubine is the main component) and alcoholic diterpenes (marrubiol), which give it excellent expectorant, antispasmodic and cough-soothing properties due to their effects on the muscles.
Mullein
Mullein's active ingredients are contained in its flowers, mainly mucilage and triterpene saponosides (verbascosaponin). The peculiarity of the Mullein phytocomplex lies in the co-presence of the two, which exert an expectorant and mucolytic action and, simultaneously, are soothing and refreshing on the mucous membranes.
Enula Campana
Enula is rich in essential oils (sesquiterpene lactones), which are excellent substances for treating coughs due to their expectorant, mucolytic, soothing and broncho-relaxant pharmacological properties.
Maidenhair
It is a fern of which the aerial part is used, as it is rich in tannins (gallitannins), mucilage and triterpenoid core saponosides. These properties have excellent expectorant, mucolytic, emollient, soothing and decongestant effects on the upper airways.
Helichrysum
Helichrysum boasts antispasmodic, mucolytic and expectorant action due to the presence of flavonoids and essential oils contained in its flowering tops. Recent studies have also shown modest antibacterial activity, acting in synergy with GSE.
Poppy
Wild Poppy flower petails contain a fair amount of mucilage and readin (a benzyl-isoquinoline alkaloid), substances with marked calming and soothing properties, thus useful in the treatment of dry coughs. Mucilages can, due to their hydrophilic characteristics, also form a light film over the walls of the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract, protecting them from irritation and thus soothing coughs.

Echinacea angustifolia
An extract rich in polysaccharides, alkylamides, and caffeic acid esters (including echinacoside) obtained from the valuable Echinacea root. It has decongestant and anti-inflammatory effects on the mucous membranes of the oropharyngeal tract, as well as stimulating natural defenses, facilitating immune response to microorganisms responsible for disease and slowing their spread. It also contributes, thanks to the presence of polysaccharides, to the formation of a soothing and protective muco-adhesive film that aids the regeneration of injured and irritated mucosal tissues.

Altea
The extract obtained from Altea root is very rich in mucilages (up to 20-35%, mainly rhamnogalacturonans, arabinans, glucans and arabinogalactans), as well as flavonoids, tannins, pectins and starches. Mucilages result in the formation of a moisturizing muco-adhesive film that protects against contact with external agents, while simultaneously having a decongestant and inflammatory effect on the mucous membranes themselves, which are particularly irritated and weakened by infection, restoring them to their physiological condition. In addition, conveying water promotes rehydration and exerts an emollient and soothing action that reduces the coughing stimulus.
Ginger
The presence of ginger helps to reduce pain caused by irritative and inflammatory states of the oral mucous membranes. In fact, it possesses extraordinary anesthetic, analgesic and pain-relieving properties.
Astragalus
Several clinical studies have shown that Astragalus root affects the immune system, in synergy with the beneficial action of Echinacea, and that it can help in the prevention and treatment of colds and flu, reducing the duration of symptoms and decreasing their magnitude through its immunomodulatory and tonic-adaptogenic actions, which are particularly important in children.
Aloe vera
The gel obtained from the Aloe vera plant boasts strong anti-inflammatory, soothing and lenitive properties. Thanks to the high presence of polysaccharides, it can have a soothing film-forming action on the mucous membranes in the mouth and throat, promoting tissue repair thanks to its healing qualities.

Erisimus
Erisymus extract has significant anti-inflammatory properties, particularly useful for irritation caused by a sore throat. In addition to its analgesic and anti-irritant properties, it also has mucolytic and expectorant effects.
Sweet Orange Water
The addition of Sweet Orange water has a soothing and relaxing effect, useful for the well-being of the upper respiratory tract, as well as an important antioxidant effect.
Grapefruit Seed Extract (GSE)
Grapefruit Seed Extract (GSE), rich in bioflavonoids, boasts strong antimicrobial properties and is characterized by its selectivity: it counteracts pathogenic microorganisms without affecting the beneficial physiological microflora, thus protecting the natural balance and defensive capacity of mucous membranes. It possesses antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal properties and is effective against viruses and bacteria responsible for respiratory tract and oropharyngeal cavity disorders, such as Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Influenza virus A2, etc.

LIFESTYLE - NUTRITION - THROAT
The human body is almost always able to overcome attacks from viruses, bacteria and fungi, as long as we keep it healthy and give it proper attention by ensuring it has all the elements it needs to function properly (vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, fats, etc.). One of the indispensable factors is making conscious choices about food and a willingness to adopt balanced behavior throughout the year, not only in situations of necessity when the symptoms of bronchitis, cold, flu, cough, sore throat, earache, etc. are already present. In order to strengthen natural defenses, it is of fundamental importance to adopt a balanced diet which is also rich in fiber: this part of food that the digestive system cannot digest represents the main and preferred nourishment for the intestinal bacterial flora that helps us protect ourselves from external agents. Accordingly, we recommend whole grains, vegetables and fruits, both cooked and raw. These are valuable foods for their fiber content, but also for the supply of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
On the other hand, foods that weaken the immune system and the intestinal flora should be avoided:
- simple sugars and refined carbohydrates, especially sweets, candies, snacks, sugary drinks, refined grains (white pasta and bread, as well as all baked goods made from refined flour)
- trans-hydrogenated fats and excess saturated fats, especially fried foods, cured meats, processed meats, dairy products and red meat.
- high-calorie foods that are rich in unhealthy fats such as hydrogenated fats (lipids that undergo a transformation known as hydrogenation to be suitable for the needs of the food industry), which are responsible for worsening the inflammation
THE BENEFITS OF
- FRUITS AND VEGETABLES. By consuming fruits and vegetables daily, elements such as antioxidants, vitamins, minerals and fiber are supplied, which are useful in controlling and lessening the overall state of inflammation, thus helping the immune system to be ready and efficient when needed. IMPORTANT. It is essential to respect the seasonality of foods because fruits and vegetables from greenhouses, or imported from distant countries, rarely reach the quality of naturally ripened ones in terms of the content of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. IMPORTANT: Cooking fruits and vegetables at high temperatures significantly reduces the concentration of vitamin C and all volatile vitamins.
- DRIED FRUIT. Nuts (especially pecans), pine nuts, almonds, cashews, etc. are valuable sources of zinc, a mineral which is essential for the body, fulfilling a number of biological roles, most importantly that of supporting the immune system. It is important to avoid zinc deficiency, which is quite common due to an unvaried diet rich in refined foods.
- FERMENTED FOODS. Sauerkraut, vegetable yogurt with no added sugars, tempeh (a food derived from soybean fermentation), water kefir, etc. contain live bacteria cultures, so-called probiotics, which contribute to the healthy intestinal flora and thus strengthen the immune system.

OTHER SUPPORTERS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM

- consuming foods of organic and/or 0-km origin
- in accordance with the above advice, following a varied diet, favoring the consumption of fruits and vegetables, preferably in season, easily digestible proteins (small fresh fish, white meat, eggs), legumes, pumpkin seeds, sunflower, flax, chia, etc., walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts, etc.
- consuming cereals, preferably whole grain but not only, because in some cases fiber prevents the absorption of minerals and other nutrients, semi-wholegrain cereals and pseudocereals (quinoa, buckwheat, amaranth)
- preferring foods that are sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as flax oil, hemp oil, oily fish (mackerel, sardines, sardines etc.), chia seeds, flax seeds, etc.
- staying adequately hydrated. Water requirements vary from individual to individual and change according to different lifestyles, type of activity and diet. An adult
- should generally drink 2 liters of water per day to maintain good health. Water is an essential element for the body because it regulates various biological functions.
- Therefore, it is important to maintain proper hydration, especially during the summer season, during sports activities and in all situations in which a lot of fluids are lost.
- avoiding abuse of gluten-containing foods, packaged foods and fried foods
- limiting sugar, sugary drinks, refined grains (white bread, white pasta, white rice, etc.)
- avoiding hydrogenated fats, limiting red meat, milk and its derivatives, and salt. When consuming them, prefer those of high quality
The notions and advice offered herein are for educational purposes only and cannot under any circumstances replace medical advice. For a complete diet, it is necessary to consult a nutritionist, who, after appropriate clinical and instrumental examination, will be able to identify the needs of the person concerned and put together a personalized diet plan.